What are T3 and T4: The Complete Guide to Your Thyroid Hormones
T3 and T4 are hormones that are secreted by your thyroid gland and have a major impact on your health. T4 is the thyroid hormone thyroxine and T3 is the hormone triiodothyronine, and they affect almost every organ in your body. T4 and T3 levels in your body are regulated by the thyroid-stimulating hormone, or TSH for short. Thyroid tests to check thyroid function usually check for abnormal levels of TSH and T4 hormones.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) are usually associated with low levels of T4 and T3. This can cause you to feel fatigued, have difficulty losing weight, feel tired, and have hair loss. An underactive thyroid is also associated with high TSH levels and low T4 levels.
An overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism is caused by high T4 and T3 levels in your bloodstream. When your thyroid secretes too much thyroid hormones you can feel restless, suffer from sleep problems, have frequent digestive upset, and increased sweating. If you suffer from hyperthyroidism, your thyroid test results will usually show low levels of TSH hormone.
This article contains a complete guide to your thyroid hormones and thyroid function. You will learn what T4 and T3 hormones do in your body and what the target range of T3 and T4 is. I will also explore why testing for free T4 levels is sometimes better than a TSH blood test.
The Thyroid Gland and What it Does
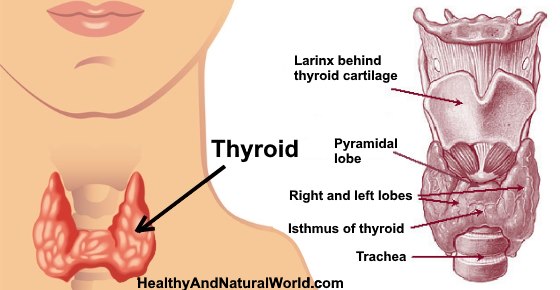
Your thyroid is an important hormonal gland in the body that has a direct impact on your metabolism. Your thyroid sits in the front part of your neck just below your voice box and is shaped like a butterfly.
Dr. Carol DerSarkissian on WebMD says that the thyroid releases hormones into the bloodstream. Your thyroid releases triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and calcitonin (produced by the parathyroid glands). From these, Dr. DerSarkissian says that T4 is the main hormone that affects growth, metabolism, and brain development.1
What is TSH?
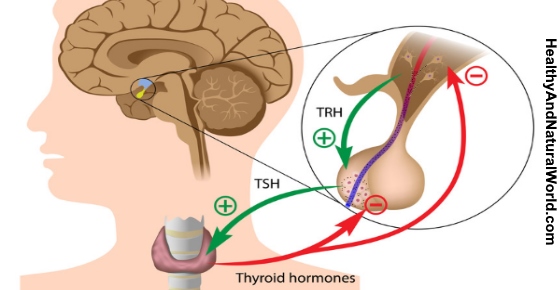
Your thyroid function depends on hormones that are released by glands at the base of your brain. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) which then stimulates the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland then secretes TSH that stimulates the thyroid to produce T3 and T4 hormones which are released into your bloodstream.
Doctors from the Cleveland Clinic explain that TSH levels can fluctuate depending on T3 and T4 levels in blood serum. For example, if your thyroid doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones (underactive thyroid), messages are sent to your pituitary gland to increase TSH levels. On the other hand, high levels of T4 and T3 hormones caused by an overactive thyroid can signal your brain to lower TSH.2
The journal Frontiers in Endocrinology describe this connection between T3, T4, and TSH as a feedback loop. Doctors say that TSH testing may not be the most accurate way to monitor thyroid health if you receive T4 thyroid replacement therapy for hypothyroidism.3
What are T3 and T4?
T3 is the thyroid hormone triiodothyronine and T4 is the thyroid hormone thyroxine.
The British Thyroid Foundation says that T3 and T4 are the two main hormones that your thyroid gland secretes. Together they affect and influence almost every cell in your body. Your thyroid usually produces more T4 hormone than T3, but T4 is converted to T3 when it reaches cells and tissues in your body. Therefore, T4 is the more important hormone to measure when testing for thyroid dysfunction.4
Let’s look in more detail at what T3 does and why T4 is the more potent hormone.
What is T3?
Doctors from the Mayo Clinic say that triiodothyronine (T3) has 3 iodine molecules in its structure. This is secreted directly by the thyroid gland and is classed as the most powerful thyroid hormone. This is because it is more metabolically active when controlling your body’s metabolism, temperature, and digestive system.5
What is Free T3 (FT3)?
Thyroid hormone binds to proteins in your body and any that isn’t is classed a free T3. The British Thyroid Foundation says that free T3 is the active part of triiodothyronine. The level of FT3 can help to diagnose hyperthyroidism and monitor replacement T3 therapy.6
What is T3 Uptake?
Sometimes, you may hear doctors talking about T3 uptake when discussing thyroid testing. What is T3 (T3RU) uptake? The book Clinical Methods says that T3RU (T3 uptake) test measures the levels of proteins in the blood that carry thyroid hormone.7 T3 uptake can help your doctor interpret the results of T3 and T4 blood tests. The T3RU test is hardly used these days because the TBG (thyroxine-binding globulin) and the free T4 blood tests are now available.
What is T4?
The thyroid gland also secretes T4, but in larger quantities than T3. Thyroxine (T4) has 4 iodine molecules attached to its molecular structure. When T4 gets into the cells of the body, it loses one molecule and becomes T3. Thyroid function tests that check both TSH and T4 levels are the most accurate ways to diagnose thyroid conditions.8
What is Free T4 (FT4)?
Similar to free T3, free thyroxine (T4) levels are the unbound levels of T4 hormone (the active part of thyroxine). You have more free T4 (FT4) in your blood than FT3. High T4 levels or low T4 levels can help to accurately diagnose hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. The book Clinical Methods says that blood tests for both TSH and T4 help to accurately assess thyroid health.7
The amount of free T4 helps doctors see how much thyroid gland hormone is available in your blood to meet your energy requirements.
Normal Levels of T3 and T4
If you show signs of abnormal thyroid function, doctors may arrange for a blood test to check FT4 levels and possibly free T3. This is usually done at the same time as a TSH blood test, or doctors may check T4 levels only if TSH blood test readings are abnormal.
Normal T3 levels (Normal Free T3 Levels and Total T3)
Dr. Jayita Poduval, who is an Ear, Nose, and Throat (EAT) specialist, says that the normal total T3 and free T3 ranges are as follows:9
Total T3 (triiodothyronine) range:
- Children: 125 – 250 ng/dL
- Adults: 80 – 220 ng/dL
Normal free T3 (FT3) range:
- Adults: 260 – 460 pg/dL (4 – 7.4 pmol/L)
Normal T4 levels (Normal Free T4 Levels and Total T4)
Testing for normal levels of T4 thyroid hormone is a common lab test along with TSH to diagnose thyroid issues. Dr. Muhammad Bader Hammami on Medscape says that total T4 (TT4) range and free T4 (FT4) range are as follows:10
Total T4 (TT4) range:
- Newborn babies up to 14 days old: 11.8 – 22.6 mcg/dL (152 – 292 nmol/L)
- Babies and older children: 6.4 – 13.3 mcg/dL (83 – 172 nmol/L)
- Adults: 5.4 – 11.5 mcg/dL (57 – 148 nmol/L)
Normal free T4 (FT4) range:
- Children and adolescents: 0.8 – 2 ng/dL (10 – 26 pmol/L)
- Adults: 0.7 – 1.8 ng/dL (9 – 23 pmol/L)
- Pregnant women: 0.5 – 1.0 ng/dL (6.5 – 13 pmol/L)
How TSH Affects T3 and T4 Levels
TSH, T4, and T3 are all connected with your thyroid function and TSH can affect thyroid hormone levels in your blood. TSH levels that are less than the normal range often indicate hyperthyroidism because your thyroid is overproducing T3 and T4. If your lab test results show high TSH levels, this can indicate that your thyroid is sluggish and there is not enough thyroid hormones.
To learn what your TSH levels mean, read my complete guide to TSH levels (including optimal thyroid levels).
High T3 and T4
Having lab test readings that show high T3 and T4 can mean that you have hyperthyroidism. Doctors will usually test FT4 levels and may also run FT3 tests if your TSH readings are low.
High T3 Symptoms
Dr. Stephanie Lee on eMedicineHealth says that significantly higher than normal T3 can be a sign of severe hyperthyroidism.11 According to the journal Clinical Endocrinology, Graves’ disease is a common cause of severe hyperthyroidism. This can cause symptoms like:12, 13
- Bulging eyes
- Thick red skin on the tops of your feet
- Inflamed eyes with a gritty feeling
- Increased sensitivity to light
High T4 symptoms
If your T4 test readings are too high, it can mean you have hyperthyroidism. According to Dr. Oliver Starr on Patient.info, classic signs of an overactive thyroid gland that secretes too much T4 hormone can include any of the following:14
- Increased irritability and restlessness
- Poor sleeping habits and difficulty getting to sleep
- Runny stools because your digestive system is working too quickly
- Losing weight without trying
- Itchy skin
- Thinning hair
- Increased sweating
- Light menstrual periods
- Shortness of breath
Low T3 and T4
When levels of T3 and T4 fall below the normal range, you will probably show signs of hypothyroidism. Mild hypothyroidism can even occur if your TSH readings are within the normal range.
Low T4 Symptoms
Dr. Gabriel Bucurescu on Medscape says that classic symptoms of an underactive thyroid that doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormone can include:15
- Feelings of weakness and fatigue
- Dry skin and hair
- Weight gain
- Problems with memory and concentration
- Tingling in the fingers or a feeling of ‘pins and needles’ in the feet
- Intolerance to the cold
Low T3 Symptoms
Usually, low T3 levels in a thyroid function test are matched by low T4 readings and elevated TSH levels. Therefore, T3 below the normal range usually means a person has hypothyroidism.
According to doctors from the American Association for Clinical Chemistry, it would be rare when blood tests show low T3 with low TSH and high T4.16
How TSH is Connected with T3 and T4 Levels
Dr. Oliver Starr on Patient.info explains that all your thyroid hormones and TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) need to work in balance. This forms what doctors call a feedback loop where the levels of thyroid hormone in your blood signal to your brain to produce more or less TSH.17
For example, if an overactive thyroid produces too much T4 or T3, the feedback loop to your brain signals to produce less TSH. The same is true if your thyroid isn’t working properly and produces too little hormone.
Doctors from the National Health Service explain the basic relationship between TSH and thyroid hormone levels:18
- Hypothyroidism: TSH high, T4 low, and T3 low or normal
- Hyperthyroidism: TSH low, T4 high or normal, and T3 high or normal
- Subclinical thyroid disease: Levels of T4 and T3 are normal but TSH is either too high or too low
- Non-thyroidal illness: TSH low, T4 low or normal, and T3 low or normal
High (Elevated) TSH and Normal T4
Lab test results that show TSH levels greater than 4.0 mU/L and T4 within the normal range can indicate subclinical hypothyroidism.
According to the journal American Family Physician, subclinical hypothyroidism could show that person is at greater risk of developing an underactive thyroid disorder. This often happens in older women and there may be no visible symptoms. Doctors treat subclinical hypothyroidism on an individual basis as thyroid hormone replacement can lead to osteoporosis.19
High TSH and Low T4
Blood test results that show TSH levels higher than the normal range and FT4 of less than 0.7 ng/dL mean that you have an underactive thyroid.
Dr. Laura J. Martin on WebMD says that some of the causes of hypothyroidism can include:20
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s disease) which is an autoimmune disorder that attacks the thyroid gland
- Inflammation of the thyroid gland
- Radiation treatment for cancer
- A lack of iodine in the diet
- Pregnancy can also cause high TSH and low T4 readings
Low TSH and High T4
Test result reading of TSH of less than 0.4 mIU/L and FT4 more than 1.8 ng/dL means that your thyroid is overactive. Hyperthyroidism is less common that an underactive thyroid, however, similar to hypothyroidism, it affects women more than men.
Dr. Carol DerSarkissian on WebMD says that some conditions that are linked to hyperthyroidism can include:21
- Antibodies in your blood that affect your thyroid (as in Graves’ disease)
- Noncancerous growths in your thyroid that cause it to swell and produce more T4
- An autoimmune condition
- Receiving too much thyroid replacement hormone
Normal TSH and Low T4
In some cases, TSH test results are within the normal range but low T4 results can occur. Dr. Louise Newson on Patient.info says that this can often happen in people who are chronically ill. The illness may affect a person’s metabolism which affects their thyroid hormone levels. This means that the pituitary gland is secreting TSH within the normal range and the thyroid is working properly. However, thyroid hormones in the body are lacking.22
Also, if you have recently had treatment for hyperthyroidism, you could have normal TSH but low T4.
Treating Hypothyroidism with Replacement T4 and T3
Doctors treat the symptoms of hypothyroidism by prescribing oral thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Some treatments for an underactive thyroid involve prescribing T4 replacements like levothyroxine sodium (brand names: Levothroid, Levoxyl, Synthroid, or Tirosint). Other treatments involve a combination of T4 and T3 replacement therapy.
According to a study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, there is a move towards using combined replacement of T4 and T3 therapies. Some doctors prefer this because the combined T4 and T3 thyroid treatments may have less impact on quality of life and treat hypothyroidism better.23
Tests for Measuring T4 and T3
The British Thyroid Foundation says that testing for thyroid dysfunction can include one or more of the following tests:6
- Testing to see if free thyroxine (FT4) is within the range of 0.7 – 1.8 ng/dL
- Free triiodothyronine (FT3) tests for the range of 260 – 480 pg/dL
- TSH and FT4 test
- Testing for thyroid antibodies to diagnose Graves’ disease or Hashimoto’s disease
Doctors recommend testing for T4 and T3 as part of a thyroid function test if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Thickening around the base of the neck
- High cholesterol
- Osteoporosis
- Feel unwell after having a baby
Read these related articles:
- How to Test Your Thyroid With a Thermometer
- TSH Levels: Normal, High, or Low (Including Optimal Thyroid Levels)
- 1 Minute At Home Thyroid Cancer Self-Test: This Can Save Your Life
Medical Sources: