Pneumonia: Is It Contagious, Causes, Symptoms and Transmission
Pneumonia is a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection of the lungs that can be contagious. If pneumonia is the result of a respiratory infection like the cold or flu virus, then pneumonia is infectious and can easily spread from person to person. Pneumonia can result in a mild to severe cough that may bring up phlegm. Droplets expelled from the mouth may contain contagious germs that can easily be passed on to other people.
Bacterial pneumonia and viral pneumonia are types of inflammatory lung infections that are contagious.
Although many types of pneumonia are spreadable, not all types of pneumonia are contagious. For example, noncontagious types of pneumonia include fungal pneumonia and aspiration pneumonia. Fungal pathogens can be breathed in from the environment and cause pneumonia but won’t be transmissible between persons. Also, certain medical conditions can cause food, saliva, or foreign objects to get stuck in the lungs and cause inflammation with a “chesty cough.”
In this article, you will learn about contagious pneumonia and what can cause it. You will also find out what you can do to prevent catching pneumonia and when the lung infection is serious enough to see a doctor.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia occurs when germs, microbes, or foreign objects infect the lungs, causing inflammation and chest discomfort. Infections causing pneumonia can affect anyone of any age.
According to researchers from the American Lung Association, pneumonia – contagious and noncontagious – describes the result of lung inflammation and is not a single disease. Inflammation of the lungs causes the air sacs to fill up with fluid, and this causes a cough as well as a possible fever and/or breathing difficulties.1
The American Lung Association also says that viral pneumonia can develop into bacterial pneumonia and can cause more severe lungs inflammation symptoms. A person is at risk of catching bacterial pneumonia because of old age, if they have a weakened immune system, or are already ill.1
Pneumonia can also develop into a serious lung disease that may require treatment in a hospital if it causes complications. Dr. Melissa Conrad Stöppler on MedicineNet says that treatment for pneumonia may be necessary to control the spread of viral or bacterial infections in the body.2
What is double pneumonia?
Double pneumonia is when viral, bacterial, or fungal infections cause pneumonia symptoms in both lungs. This is also referred to as bilateral pneumonia. Double pneumonia caused by bacteria or viruses can be just as contagious as pneumonia in the left lung or right lung (single pneumonia).4
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
You can catch pneumonia very easily if you are near a person who has a form of infectious pneumonia. Viruses and bacterial infections that cause lung inflammation and respiratory illnesses like the flu cause contagious pneumonia.
For example, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention says that the flu is highly contagious and is easily transmittable.3 A person who “catches” the flu virus can develop infectious bronchitis or symptoms of mild to severe pneumonia.
Many types of bacterial pneumonia can also be passed from one person to another, although bacterial forms of pneumonia aren’t as contagious as viral lung infections. However, doctors say that tuberculosis that causes bacterial pneumonia is very infectious.2
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Pneumonia?
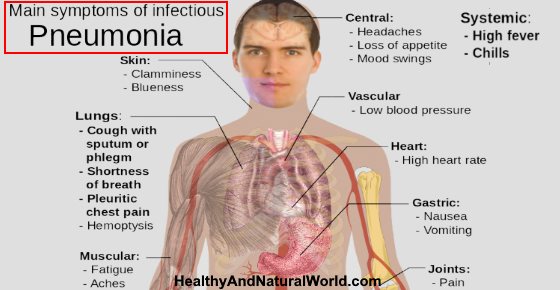
It’s important to recognize the symptoms and signs of pneumonia to make sure that the lung disease doesn’t progress and cause further complications. Pneumonia can cause symptoms similar to bronchitis, but is usually more severe and leaves a person feeling fatigued.
According to doctors from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the signs and symptoms of pneumonia can include the following:5
- High fever with or without shaking chills
- Coughing up green or yellow-colored mucus (phlegm)
- Shortness of breath and breathing difficulties when engaging in day-to-day activities
- Coughing or breathing deeply causes chest pains
If any of your symptoms don’t improve with treatment or suddenly get worse, you should see your doctor for a checkup.
If left untreated, pneumonia can cause complications that can even be life-threatening. Some serious pneumonia complications can include:5
- Bacteria from a bacterial lung infection enters the bloodstream and causes septic shock
- Pleurisy along with sharp chest pains when breathing deeply
- Kidney problems and serious respiratory problems
How Long is Pneumonia Contagious?
You can catch pneumonia from someone who has a viral or bacterial lung infection a day or so before they start showing symptoms.
Dr. Charles Patrick Davis on MedicineNet says that pneumonia can be contagious for up to a weak or so with viral pneumonia. Usually, viral pneumonia is less contagious as the symptoms begin to go away. This usually means that pneumonia is no longer infectious a day or so after the fever has gone.6
Depending on the type of bacterial lung infection, pneumonia caused by bacteria can be contagious for between 1 to 2 days after taking antibiotics. However for tuberculosis it can take two weeks or more after taking antibiotics before the person is no longer contagious.6
This means that the incubation period for pneumonia can be anywhere from 2 to 14 days, depending on the severity of your infection. It’s also not uncommon for a cough caused by pneumonia to persist for a few weeks after a person is no longer contagious.
How do you Spread Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is spread through contact with infected respiratory fluid that enters your mouth, eyes, or nose. This means that you can easily catch pneumonia from someone else if you touch infected surfaces and then touch your own mouth or nose.
According to doctors from the National Health Service, pneumonia also spreads through being in close contact when a person coughs or sneezes. Droplets of infected fluid can land on or near your mouth or nose, and the respiratory infection can find its way into your lungs.7
Staff from the Mayo Clinic report that pneumonia that spreads between people is often referred to as community-acquired pneumonia. This is when viral, bacterial, or fungal pneumonia gets transmitted between people outside of a hospital or medical facility (which is referred to as hospital-acquired pneumonia). This can cause mild to severe symptoms of lung infections that last from a few days to several weeks.8
How to prevent catching pneumonia from someone who has it
Because viral and bacterial lung infections can be highly contagious, it’s important to try and prevent the spread of pneumonia.
For example, you can prevent catching an infectious respiratory infection if you stay away from people who are showing symptoms of the cold or flu like coughing and sneezing. Another way to prevent catching pneumonia is to wash your hands often. This helps to stop the bacteria and viruses that cause pneumonia spreading by getting into your respiratory tract.18
What is Walking Pneumonia?
Walking pneumonia is any type of pneumonia that causes mild respiratory symptoms like sneezing or coughing. This type of lung inflammation is referred to as “walking pneumonia” because a person usually can go about their daily activities showing few or no symptoms of pneumonia.
According to Dr. Carol DerSarkissian on WebMD, anyone can get walking pneumonia and it usually causes cold-like symptoms.9
Symptoms and causes of walking pneumonia
Dr. Carol DerSarkissian says that a bacterial infection of the Mycoplasma pneumonia strain of bacteria is usually the cause of walking pneumonia. Usually, the incubation period of walking pneumonia is between 2 and 4 weeks before you start to show symptoms.9
Signs that you have walking pneumonia can be any of the following:
- Pain under your left rib cage or right rib cage when breathing deeply
- Sudden attacks of coughing
- Flu-like symptoms like fever, sore throat, and headaches
- Fatigue that lasts after your respiratory infection symptoms have gone
Is walking pneumonia contagious?
Walking pneumonia is contagious if it is caused by a bacterial or viral infection. Usually, walking pneumonia is spread among people living in close proximity. For example, walking pneumonia spreads quickly in schools, dorms, shared accommodation, or nursing homes.
How long is walking pneumonia contagious?
You can spread walking pneumonia to other people for up to 10 days after first showing symptoms of a lung infection. However, bacterial pneumonia isn’t as contagious as viral pneumonia and may take extended contact with an infected person for it to get transmitted.
What is Bacterial Pneumonia?
Bacterial pneumonia is a communicable respiratory infection that can produce mucus in the lungs. Dr. George Schiffman on eMedicineHealth says that lung infections cause inflammation in the respiratory tract that can affect the amount of oxygen the body gets. This can result in an infectious type of pneumonia, especially if it is caused by tuberculosis or Mycoplasma pneumoniae bacteria.10
Other symptoms of bacterial pneumonia can include:
- Chest pains when sneezing or breathing deeply
- Feeling short of breath
- Fever
- Pleurisy and accompanying symptoms
Is bacterial pneumonia contagious?
Bacterial pneumonia can be contagious depending on the type of bacteria causing the respiratory infection. Dr. George Schiffman says that although most kinds of bacterial pneumonia are infectious, they are not highly contagious.10
What is Viral Pneumonia?
Various types of viruses can infect the lungs and respiratory tract resulting in viral pneumonia. This type of pneumonia is a common complication of suffering from the influenza virus or the common cold.
According to the journal The Lancet, viral pneumonia is common among children, the elderly, and people with a compromised immune system. Some of the viruses that cause viral infections in the lungs are rhinovirus, bocavirus, or influenza virus. Viral pneumonia is also a type of community-acquired pneumonia and a reason for “walking pneumonia.”11
Some of the symptoms of viral pneumonia can include:
- A low fever, usually less than 102°F (38.8°C)
- A persistent cough that may bring up small amounts of phlegm
- General fatigue
- Aching muscles
Is viral pneumonia contagious?
You are usually contagious with viral pneumonia for as long as your symptoms last. Usually, sputum, saliva, or mucus that you cough up will contain infectious germs that can spread from person to person.
Dr. Charles Patrick Davis (quoted earlier) says that viral pneumonia is infectious for as long as you have a fever. However, depending on the type of respiratory viral infection, your pneumonia may still be spreadable for up to a week after symptoms have gone. A cough in itself isn’t a sign that viral pneumonia is still contagious.6
What is Fungal Pneumonia?
Fungal pneumonia is a noncontagious infection in your respiratory tract that is caused by breathing in spores. These spores infect the air sacs in the lungs and cause inflammation which results in symptoms of pneumonia.
According to Dr. Romeo A. Mandanas, a researcher at the Integris Cancer Institute of Oklahoma, fungal pneumonia is a less-common type of community-acquired pneumonia than the viral or bacterial varieties. Fungal pathogens can affect healthy individuals as well as people with compromised immune systems.12
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention reports that “valley fever” (coccidioidomycosis) is a type of fungal pneumonia common in the southern states in the U.S. This type of fungal pneumonia is caused by breathing in spores from the soil.13
Some of the symptoms of fungal pneumonia can include:14
- A dry cough that is difficult to get rid of
- Breathlessness, especially after physical exertion
- Chest discomfort
- Inflamed and sore joints with arthritis-like pain
- Muscle aches
- Rash
Is Pneumonia Contagious After Antibiotics?
The answer to the question: “is pneumonia contagious after antibiotics?” depends on the type of pneumonia that is causing your cough.
Doctors often prescribe antibiotics for bacterial infections of the lungs or for viral pneumonia that has turned into bacterial pneumonia. Doctors from the National Health Service say that usually pneumonia is no longer infectious about 24 hours after taking antibiotics. However, the length of time a person is infectious can vary.15
For example, some antibiotics take longer to work in some people than other people. This means that you could still spread bacterial pneumonia to another person more than 24 hours after starting antibiotics. Or, if you have viral pneumonia together with bacterial pneumonia, you may still pass on viral infections even though you are taking antibiotics.
Can Pneumonia Go Away on its Own?
Mild forms of walking pneumonia may go away on their own without the use of medication. According to doctors at the Cleveland Clinic, some mild respiratory bacterial infections often clear up by themselves after a few weeks. However, you need to see a doctor if your symptoms of pneumonia become severe.16
Usually, the symptoms of viral pneumonia are less severe and should clear up on their own. Dr. Carol DerSarkissian on WebMD says that no medication is usually prescribed to treat the symptoms of viral pneumonia and the infection has to run its course. With viral pneumonia, a person should stay at home for at least a few days to get plenty of rest and drink plenty of fluids.17
How Long does it Take for Pneumonia to Go Away?
The length of time that it takes for the symptoms of pneumonia to disappear depends on the type of lung infection you have and its severity.
Dr. Carol DerSarkissian (quoted earlier) says that you may not start feeling better for up to 3 weeks while recovering from pneumonia. However, some factors can also mean that it takes longer than usual to completely recover from pneumonia. Some of these factors can include:18
- Age and strength of immune system. If you are already ill or are a senior person, your symptoms of pneumonia can be more severe and take longer to go away. If you are elderly, you should see a doctor as soon as possible when you develop the first signs of pneumonia.
- Type of infectious pneumonia. Usually, bacterial pneumonia causes more severe symptoms and complications and takes longer to treat.
- Home care for pneumonia. It’s important to get plenty of rest to allow your body to recover quicker from a lung infection. Making sure you avoid irritating your lungs and drinking plenty of fluids are good ways to make pneumonia go away quicker.
Is pneumonia curable?
With the proper treatment and home care, pneumonia is curable.
Researchers from the American Lung Association say that usually viral pneumonia is cured with getting plenty of rest at home and taking home remedies to loosen phlegm. Doctors will treat mild to severe bacterial pneumonia with antibiotics to kill off infection-causing bacteria and prevent symptoms worsening.
In all cases of pneumonia, it’s important to eat a well-balanced diet, incorporating foods that can cleanse your lungs. Some of the best foods to eat for healthy lungs are green-leafy vegetables, foods containing omega-3 fatty acids, garlic, and flavonoid-rich foods.
How many days does it take to recover from pneumonia?
Dr. Gregory Thompson on WebMD says that generally, it takes up to 3 weeks for pneumonia to go away in healthy people. However, it may take between 6 and 8 weeks, or even longer, for pneumonia symptoms to go away in older adults or people with underlying health issues.18
When to See a Doctor
Pneumonia can develop into a serious respiratory infection that causes unpleasant complications. Usually, using home remedies to treat chest infections at the first signs of a viral or bacterial chest infection help to prevent pneumonia becoming worse.
In some cases, you may need to visit your doctor to get your lung infection symptoms checked out. Dr. Laurence Knott on Patient.info recommends seeing a doctor for pneumonia in the following circumstances:19
- The symptoms of pneumonia get worse despite using home remedies.
- You start to cough up thick phlegm or mucus that is yellow, green, brown, or has streaks of blood.
- You get no relief from a “chesty” cough after 4 weeks.
- You frequently have bouts of bronchitis or other chest infections.
- You have shortness of breath, dizziness, fast breathing, or chest pains.
Read my other related articles:
- Early Signs of Lung Disease & How to Strengthen Your Lungs
- The Most Effective Foods to Cleanse your Lungs (Research Based)
- Types of Mucus: What the Color of Your Mucus Tells About Your Health
- Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments
Medical References
